Key Takeaways:
- Understanding and mitigating fall hazards is crucial for worker safety.
- Proper training and equipment significantly reduce the risk of falls.
- Regular inspections and maintenance of safety gear are essential.
- Employers must comply with safety regulations to avoid penalties.
Safety when working at heights is essential across industries such as construction, telecommunications, and building maintenance. Implementing practical, proven protection measures not only safeguards workers from accidents but also ensures compliance with key industry standards. Partnering with trusted equipment providers such as Platforms and Ladders can further support safety initiatives and help organizations maintain high standards of worker protection.
Effective safety protocols serve dual purposes. They reduce workplace injuries and create a more productive, law-abiding environment. Employees must navigate countless hazards daily, and the proper use of equipment, alongside a rigorous safety culture, gives them the confidence to perform their duties efficiently.
Beyond compliance, investing in equipment and well-structured training lays the foundation for a work environment that values human life and productivity equally. Many companies that stay proactive in their approach to fall protection not only experience fewer incidents but also cultivate stronger teams invested in mutual safety and respect.
Modern industry standards continue to evolve, demanding greater attention to detail and responsibility from both employers and employees. By staying up to date with the latest advancements and guidance, organizations demonstrate their commitment to their people and their craft.
Understanding Fall Hazards
Falls from heights continue to be a leading source of severe workplace injuries and fatalities. Common hazards include unguarded edges, floor openings, unstable platforms, and improper equipment use. According to data from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), falls accounted for hundreds of worker deaths in recent years, especially in construction. Thorough hazard assessment is a critical first step in risk mitigation on any job site.
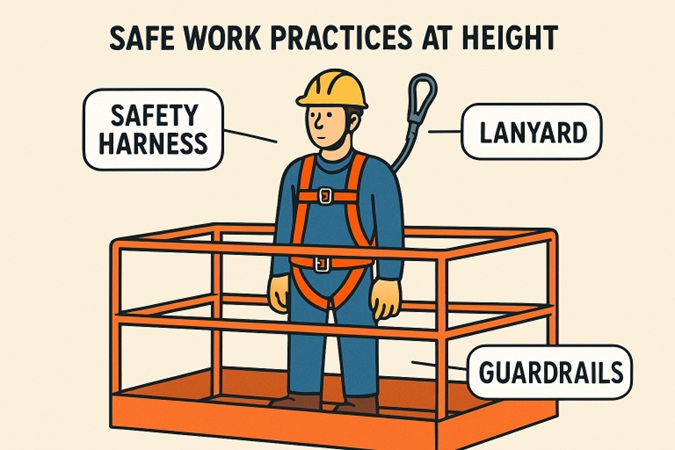
Implementing Effective Fall Protection Systems
Selecting and installing appropriate fall protection systems is a responsibility shared by employers and safety managers. The three principal systems are:
- Guardrails: Physical barriers designed to shield workers from unintentional falls, especially around open sides and elevated platforms.
- Fall Restraint Systems: Engineered to restrict the worker’s movement, preventing them from reaching hazardous edges or areas.
- Fall Arrest Systems: Last line of defense systems that safely stop a worker’s fall and minimize injury, usually utilizing harnesses and lanyards.
The right solution depends on the nature of the work, the workplace environment, and the specific site risks identified in preliminary assessments. Consulting third-party guidelines or working with experienced vendors is recommended for unique situations.
Training & Education
Effective fall prevention is only possible when everyone involved understands the challenges and how to overcome them. Comprehensive safety training programs teach workers to identify hazards, properly use fall protection equipment, and respond in emergencies. Key components of quality training include:
- Correct selection, fitting, and use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Recognition of changing job site conditions and proactive hazard identification.
- Clear guidance for emergency response and rescue protocols.
Ongoing refresher courses help keep knowledge up to date as technology, regulations, and best practices evolve. Workers should always feel empowered to request additional training or clarification when safety is in question.
Regular Inspections & Maintenance
Properly functioning fall protection equipment is essential at all times. Routine inspections of harnesses, lanyards, anchor points, and guardrails must be documented and acted upon promptly. Workers should be trained to recognize signs of wear, damage, or improper installation. All faulty equipment needs immediate repair or replacement to prevent lapses in protection and ensure ongoing compliance with safety standards, as further explained by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Compliance With Safety Regulations
Compliance with regulatory standards is more than a legal mandate; it protects both workers and the business itself. OSHA requirements specify fall protection for employees working at elevations of 4 feet in general industry workplaces, 5 feet in shipyards, and 6 feet in construction. Fines for non-compliance can be substantial, but the greater risk lies in preventable injuries or loss of life. Regular site audits, thorough record-keeping, and a proactive approach to regulatory changes ensure compliance.
Emerging Technologies In Fall Protection
The market for fall protection innovations is expanding rapidly. Wearable sensors, smart harnesses, and helmet detection systems leverage real-time data to track worker positioning and activity, alerting them or supervisors to potential hazards before an incident occurs. Artificial intelligence tools can analyze work patterns to predict when and where risks are rising. Adopting these advances translates to reduced incidents, better traceability, and timely intervention, keeping every job site at the forefront of safety best practices.
Case Study: Successful Implementation Of Safety Measures
In Scottsdale, Arizona, a roofing contractor aimed to set a new safety standard by investing in state-of-the-art fall protection and reinforced scaffolding. This initiative included a formal partnership with industry experts, hands-on training, frequent inspections, and a system for worker feedback. As a result, the workplace reported zero lost time incidents, improved project efficiency, and attracted new talent impressed by the company’s reputation for prioritizing health and well-being.
Conclusion
A strategic approach to working at heights, focusing on hazard identification, comprehensive training, regular equipment inspections, and full regulatory compliance, forms the backbone of workplace safety. By embracing emerging technologies and investing in continuous improvement, employers demonstrate commitment to both productivity and the protection of their teams. Workers, in turn, gain the knowledge, confidence, and resources needed to carry out their tasks in secure conditions, benefiting everyone involved.
